function of dna polymerase 1 - characteristics of dna polymerase : 2024-10-30 function of dna polymerase 1Pol I mainly functions in the repair of damaged DNA. Structurally, Pol I is a member of the alpha/beta protein superfamily, which encompasses proteins in which α-helices and β-strands occur in irregular sequences. E. coli DNA Pol I consists of multiple domains with three distinct enzymatic activities. Three domains, often referred to as thumb, finger and palm domain work together to sustain DNA polymerase activity. A fourth domain next to the palm domain contains an function of dna polymerase 1Apps --> Settings --> Networks --> Call. Tap Wi-Fi Call --> Connection Settings. Select the desired connection preference here: Wi-Fi prefers mobile networks. You now know how to activate Wi-Fi calling on the LG V30 and thus use the W-Lan network for telephoning.
Max Stats Hindering Nature: Lv. 50: 144 - 191: 81 - 124: 83 - 126: 104 - 146: 95 - 137: 58 - 100: Lv. 100: 278 - 372: 159 - 243: 162 - 247: 204 - 288: 186 - 270: 112 - 197: Max Stats Neutral Nature: Lv. 50: 144 - 191: 91 - 138: 93 - 140: 116 - 163: 106 - 153: 65 - 112: Lv. 100: 278 - 372: 177 - 271: 181 - 275: 227 - 321: 207 - 301: 125 - 219 .
function of dna polymerase 1Aug 3, 2023 — The ultimate function of DNA polymerase is to synthesize new DNA by the process of replication. Due to which the transfer of genetic information from one generation to another is possible. It also .Lesson 2: Replication. Antiparallel structure of DNA strands. Leading and lagging strands in DNA replication. Speed and precision of DNA replication. Semi-conservative replication. .DNA polymerase I, which is usually prepared from E. coli. DNA polymerase I, has DNA polymerase activity, so this enzyme can attach to a short single-stranded region (or nick) .Nov 13, 2019 — DNA polymerases are vital for the synthesis of new DNA strands. Since the discovery of DNA polymerase I in Escherichia coli, a diverse library of mammalian DNA .
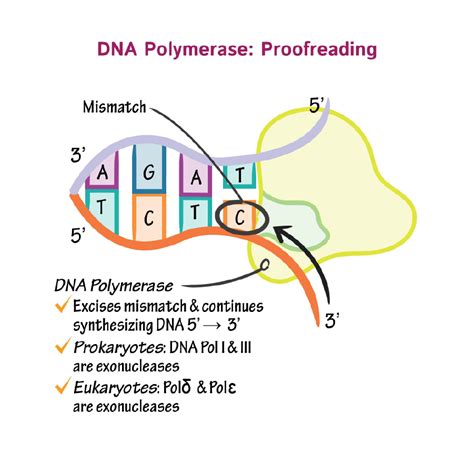
The primary role of DNA polymerases is to accurately and efficiently replicate the genome in order to ensure the maintenance of the genetic information and its faithful transmission .A DNA polymerase is a member of a family of enzymes that catalyze the synthesis of DNA molecules from nucleoside triphosphates, the molecular precursors of DNA.These enzymes are essential for DNA replication . Polymerase Family C Function. While DNA polymerase C functions are only found in bacteria, we should never forget that bacteria outnumber human cells by ten to one on and within the average body. . Properties of DNA Polymerase. DNA polymerase proofread. They check their work and cleave out unwanted or wrong nucleotides form the chain. DNA polymerase can only initiate the . DNA polymerase adds nucleotides onto the 3'OH end of the preceding nucleotide and carries out synthesis in the 5' to 3' direction down the length of the DNA. The result of DNA polymerase function .As discussed in Chapter 3, DNA replication is a semiconservative process in which each parental strand serves as a template for the synthesis of a new complementary daughter strand. The central enzyme involved is DNA polymerase, which catalyzes the joining of deoxyribonucleoside 5′-triphosphates (dNTPs) to form the growing DNA chain. However, .Ogawa, T., & Okazaki, T. Function of RNase H in DNA replication revealed by RNase H defective mutants of Escherichia coli. Molecular and General Genetics 193 , 231–237 (1984) Okazaki, R., et al .The functions of the subunits of the replication machine are summarized in Figure 5-21. Two DNA polymerase molecules work at the fork, one on the leading strand and one on the lagging strand. . These include (1) DNA polymerase and DNA primase to catalyze nucleoside triphosphate polymerization; (2) DNA helicases and single-strand DNA .Matthew Meselson (1930–) and Franklin Stahl (1929–) devised an experiment in 1958 to test which of these models correctly represents DNA replication (Figure 11.5).They grew E. coli for several generations in a medium containing a “heavy” isotope of nitrogen (15 N) that was incorporated into nitrogenous bases and, eventually, into the DNA. This labeled the .DNA: Structure, Function and Regulation; Epigenetics and Chromatin Biology; Experimental and Computational Methods and Resources; Glycobiology and Extracellular Matrices . Perhaps the best studied of these families is the DNA polymerase I (pol I)1 or A polymerase family, which includes the Klenow fragments of Escherichia coli and a . Main Difference – DNA Polymerase 1 vs 3. DNA polymerase 1 and 3 are two types of DNA polymerases involved in prokaryotic DNA replication.DNA polymerases assist the synthesis of a new DNA strand by assembling the nucleotides to the parent strand. Both DNA polymerase 1 and 3 possess replicative activity in the 5’ to 3’ direction. DNA polymerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the formation of new DNA strands by adding nucleotides to the existing DNA template strand. The enzyme also plays a role in repairing damaged DNA. The function of DNA polymerase is essential for passing on genetic information. The first known DNA polymerase, DNA polymerase I (Pol I), was isolated from Escherichia coli 1,2 and was shown to faithfully copy template DNA sequences 3.This discovery, made by Arthur Kornberg . Kornberg's additional work concerning DNA synthesis includes the elucidation of the proofreading and editing functions of DNA polymerase and the discovery of single-strand binding protein, primase, and DNA polymerase III holoenzyme. Later, Kornberg switched his research focus from DNA replication to inorganic polyphosphate (poly(P)), .DNA polymerase (DNAP) is a type of enzyme that is responsible for forming new copies of DNA, in the form of nucleic acid molecules. Nucleic acids are polymers, which are large molecules made up of .
function of dna polymerase 1 DNA polymerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the formation of new DNA strands by adding nucleotides to the existing DNA template strand. The enzyme also plays a role in repairing damaged DNA. The .

The first known DNA polymerase, DNA polymerase I (Pol I), was isolated from Escherichia coli 1,2 and was shown to faithfully copy template DNA sequences 3.This discovery, made by Arthur Kornberg . Kornberg's additional work concerning DNA synthesis includes the elucidation of the proofreading and editing functions of DNA polymerase and the discovery of single-strand binding protein, primase, .DNA polymerase (DNAP) is a type of enzyme that is responsible for forming new copies of DNA, in the form of nucleic acid molecules. Nucleic acids are polymers, which are large molecules made up of . DNA Polymerase 1 . Prokaryotes, such as bacteria, possess an enzyme called DNA polymerase I, sometimes known as Pol I, which plays a role in the replication and repair of DNA.Since it was the first DNA polymerase to be found and examined, it is known as “DNA polymerase 1”. Arthur Kornberg along with other researchers .
The Space Jockey in Alien is old enough to be fossilised. Possibly by the same events that wiped out the Engineers in Prometheus (2000 years ago according to Shaw's carbon dating) but too close to Alien's dates to be the same one. The planets have different names: LV-223 in Prometheus and LV-426 in Alien.
function of dna polymerase 1